Your cart is currently empty!
RS422/RS485 Communication Topologies and the Versa-Tap RS422/RS485 Sniffer
Full Duplex 4-wire RS422/RS485 Point to Point Connection
The simplest and most common RS422/RS485 interface is the 4-wire full-duplex point to point connection shown below. With this signaling arrangement, communication is functionally similar to that of RS232 with the improved performance provided by differential signaling.
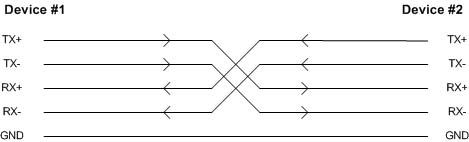 Full-Duplex Point to Point Connection
Full-Duplex Point to Point Connection
Half Duplex 2-wire RS422/RS485 Point to Point Connection
The 2-wire half-duplex point to point connection saves cabling cost at the expense of increased protocol complexity. With this signaling arrangement, the two devices must use a protocol to share the same physical wire for message transmission. This is typically done in a master/slave arrangement where the master device sends commands to the slave, and then tri-states its RS422/RS485 driver while the slave responds. The slave then turns on its driver, responds to the command, and then tri-states it’s driver in preparation for the next command.
 Half-Duplex Point to Point Connection
Half-Duplex Point to Point Connection
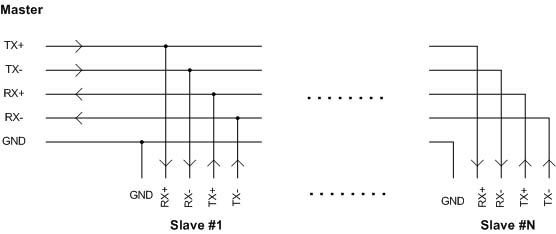
4-wire RS422/RS485 Multi-drop Connection
The 4-wire multi-drop connection supports networking where a master device communicates with multiple slaves. With this signaling arrangement the master broadcasts messages to all the slaves simultaneously using a slave address in the command message to address the slaves individually. Each slave listens to all the commands and responds when it detects a match with its pre-designated an address. The slave then turns on its driver, responds to the command, and then tri-states it’s driver in preparation for the next command.
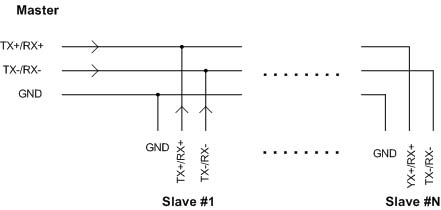
2-wire RS422/RS485 Multi-drop Connection
Like the 4-wire multi-drop connection the 2-wire multi-drop connection supports networking where a master device communicates with multiple slaves. With this signaling arrangement the master broadcasts messages to all the slaves simultaneously, typically using a slave address in the command message to address the slaves individually, then tri-states its RS422/RS485 driver while the slave responds. Each slave listens to all the commands and responds when it detects a match with its pre-designated address. The slave then turns on its driver, responds to the command, and then tri-states it’s driver in preparation for the next command.
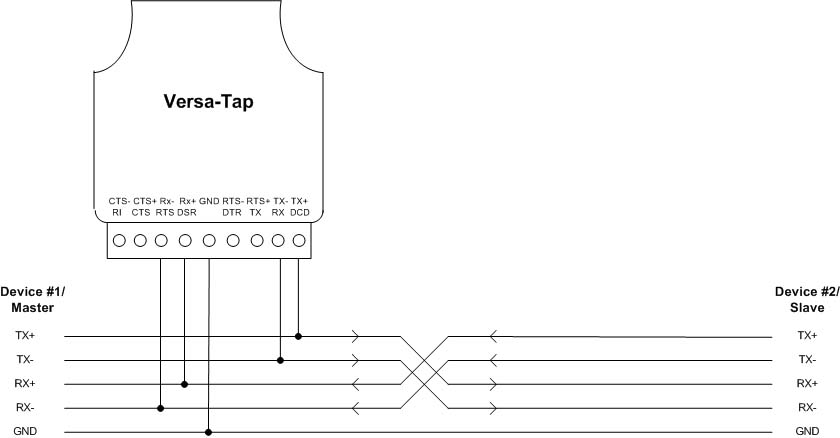
Versa-Tap Connections for 4-wire RS422/RS485 Interface
The Versa-Tap connections are the same for the 4-wire point to point and 4-wire multi-drop configurations. Connect the Versa-Tap TX+ and TX- terminals to the RS422/RS485 master TX+ and TX- signals and the Versa-Tap RX+ and RX- terminals to the RS422/RS485 master RX+ and RX- signals. Note that RS422/RS485 “+” and “-“ signals are sometimes referred to as “A” and “B” respectively.
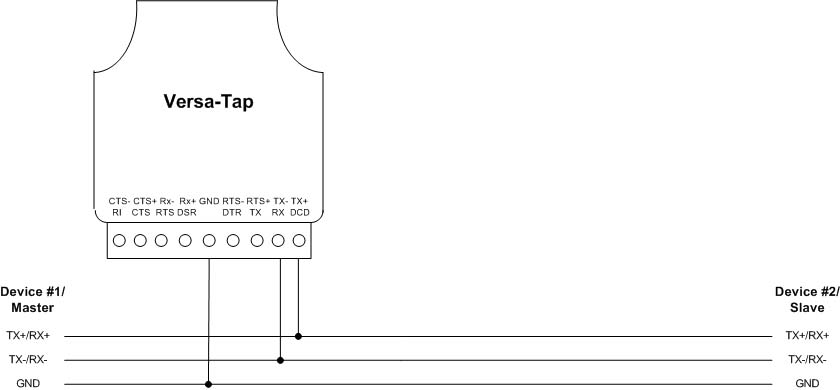
Versa-Tap Connections for 2-wire RS422/RS485 Interface
The Versa-Tap connections are the same for the 2-wire point to point and 2-wire multi-drop configurations. Connect the Versa-Tap TX+ and TX- terminals to the RS422/RS485 master TX+ and TX- signals. Note that RS422/RS485 “+” and “-“ signals are sometimes referred to as “A” and “B” respectively.